Page 804 - TNFlipTest
P. 804
NS6 Neurosurgery
CBF=CPP/CVR CPP=MAP–ICP
MAP Targets in Trauma
Traumatic brain injury: MAP >80 mmHg Spinal cord injury: MAP between 85-90 mmHg in first 7 d post injury
Autoregulation: CBF maintained despite change in CPP
Intracranial Pressure Dynamics Toronto Notes 2019 Cerebral Blood Flow
• brainreceivesabout15%ofcardiacoutput(~750mL/min)
• CBFisthevitalparameterforbrainfunctionanddependsoncerebralperfusionpressure(CPP)and
cerebral vascular resistance (CVR)
• CPPisthedifferencebetweenmeanarterialpressure(MAP)andintracranialpressure(ICP)(normal
CPP >50 mmHg)
• cerebralautoregulation:mechanismthatmaintainsconstantCBFdespitechangesinCPP,unless:
■ high ICP such that CPP <40 mmHg
■ MAP >150 mmHg or MAP <50 mmHg (these setpoints can be higher in hypertensives, thus
important to avoid hypotension)
■ increased CO2 = increased CBF via vasodilation ■ O2 <50 mmHg = increased CBF via vasodilation ■ brain injury: e.g. SAH, severe trauma
ICP Measurement
• normalICP10-15mmHgforadult,3-7mmHgforchild,1.5-6mmHgforinfant;varieswithpatient position
• moderateelevation>20mmHg • severe elevation >40 mmHg
Acute Monitoring
• indicationsinclude:severeTBI(GCS<8T)+abnormalCT;normalCTundersomeconditions
• methods:“goldstandard”isintraventricularcatheter,(externalventriculardrain(EVD)),isthemost
accurate method and allows therapeutic drainage of CSF. Non-invasive methods (including transcranial Doppler, CT/MRI, fundoscopy etc) fail to measure ICP accurately enough to be used as routine measurement techniques
Chronic Monitoring
• fibre-opticmonitor(intraventricular,intraparenchymal,subdural),subarachnoidbolt(Richmond screw), and epidural monitor
Elevated ICP
Etiology
• pathologicstructure
■ intracranial mass (tumour, cyst) ■ cerebral edema
◆ vasogenic: BBB compromised (meningitis, hypertensive encephalopathy, tumour, late ischemia) ◆ cytotoxic: BBB intact (cell death in: early ischemia, brain injury, encephalitis, status epilepticus) ◆ interstitial: transudation of CSF into peri-ventricular white matter in hydrocephalus
◆ osmotic: osmotic gradient increases intracellular free H2O (acute hyponatremia, hepatic
encephalopathy)
■ other space occupying lesions: depressed skull fracture, foreign body, pus/empyema
• increasedintracranialbloodvolume
■ space occupying blood: epidural and subdural hematomas, intraparenchymal and subarachnoid
hemorrhages
■ venous obstruction (venous sinus thrombosis, superior vena cava syndrome, cor pulmonale, venous
sinus compression)
■ impaired autoregulation (hypotension, HTN, brain injury, status epilepticus) ■ vasodilatation (increased pCO2/decreased pO2/decreased extracellular pH)
• increasedintracranialCSFvolume(hydrocephalus,seeTable6)
■ non-obstructive: increased production (rare, choroid plexus papilloma), decreased absorption ■ obstructive: blockage in CSF pathway
• idiopathicintracranialHTN(pseudotumourcerebri)–seeIdiopathicIntracranialHypertension,NS8
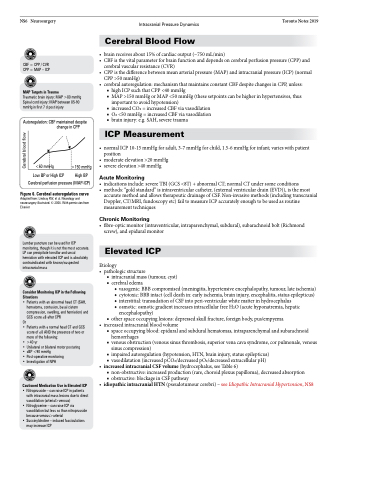
<60 mmHg
Low BP or High ICP
>150 mmHg High BP
Cerebral perfusion pressure (MAP-ICP)
Figure 6. Cerebral autoregulation curve
Adapted from: Lindsay KW, et al. Neurology and neurosurgery illustrated. © 2004. With permission from Elsevier
Lumbar puncture can be used for ICP monitoring, though it is not the most accurate. LP can precipitate tonsillar and uncal herniation with elevated ICP and is absolutely contraindicated with known/suspected intracranial mass
Consider Monitoring ICP in the Following Situations
• Patients with an abnormal head CT (SAH,
hematoma, contusion, basal cistern compression, swelling, and herniation) and GCS score ≤8 after CPR
Or
• Patients with a normal head CT and GCS
score of ≤8 AND the presence of two or
more of the following:
• >40 yr
• Unilateral or bilateral motor posturing
• sBP <90 mmHg
• Post-operative monitoring
• Investigation of NPH
Cautioned Medication Use in Elevated ICP
• Nitroprusside – can raise ICP in patients with intracranial mass lesions due to direct vasodilation (arterial>venous)
• Nitroglycerine – can raise ICP via vasodilation but less so than nitroprusside because venous>arterial
• Succinylcholine – induced fasciculations may increase ICP
Cerebral blood flow