Page 872 - TNFlipTest
P. 872
OB32 Obstetrics
Normal Labour and Delivery
Toronto Notes 2019
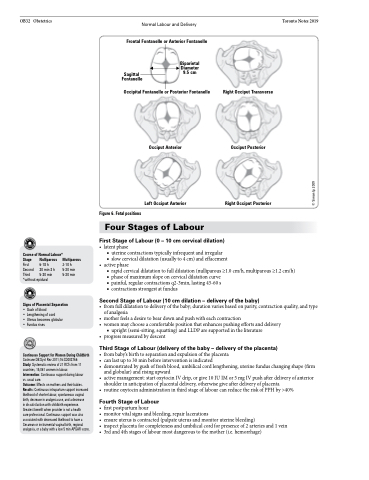
Frontal Fontanelle or Anterior Fontanelle
Sagittal Fontanelle
Biparietal Diameter 9.5 cm
Figure 6. Fetal positions
Occipital Fontanelle or Posterior Fontanelle
Right Occiput Transverse
Occiput Posterior
Right Occiput Posterior
Occiput Anterior
Left Occiput Anterior
Four Stages of Labour
First Stage of Labour (0 – 10 cm cervical dilation)
Course of Normal Labour*
• latentphase
■ uterine contractions typically infrequent and irregular
■ slow cervical dilatation (usually to 4 cm) and effacement
• active phase
■ rapid cervical dilatation to full dilatation (nulliparous ≥1.0 cm/h, multiparous ≥1.2 cm/h) ■ phase of maximum slope on cervical dilatation curve
■ painful, regular contractions q2-3min, lasting 45-60 s
■ contractions strongest at fundus
Second Stage of Labour (10 cm dilation – delivery of the baby)
• fromfulldilatationtodeliveryofthebaby;durationvariesbasedonparity,contractionquality,andtype of analgesia
• mother feels a desire to bear down and push with each contraction
• women may choose a comfortable position that enhances pushing efforts and delivery
■ upright (semi-sitting, squatting) and LLDP are supported in the literature • progressmeasuredbydescent
Third Stage of Labour (delivery of the baby – delivery of the placenta)
• frombaby’sbirthtoseparationandexpulsionoftheplacenta
• can last up to 30 min before intervention is indicated
• demonstratedbygushoffreshblood,umbilicalcordlengthening,uterinefunduschangingshape(firm
and globular) and rising upward
• activemanagement:startoxytocinIVdrip,orgive10IUIMor5mgIVpushafterdeliveryofanterior
shoulder in anticipation of placental delivery, otherwise give after delivery of placenta
• routine oxytocin administration in third stage of labour can reduce the risk of PPH by >40%
Fourth Stage of Labour
• firstpostpartumhour
• monitor vital signs and bleeding, repair lacerations
• ensure uterus is contracted (palpate uterus and monitor uterine bleeding)
• inspectplacentaforcompletenessandumbilicalcordforpresenceof2arteriesand1vein • 3rdand4thstagesoflabourmostdangeroustothemother(i.e.hemorrhage)
Stage
Nulliparous
Multiparous
2-10 h 5-30 min 5-30 min
Signs of Placental Separation
• Gush of blood
• Lengthening of cord
• Uterus becomes globular • Fundus rises
Continuous Support for Women During Childbirth
Cochrane DB Syst Rev 2011;16:CD003766 Study: Systematic review of 21 RCTs from 11 countries, 15,061 women in labour. Intervention: Continuous support during labour vs. usual care.
Outcome: Effects on mothers and their babies. Results: Continuous intrapartum support increased likelihood of shorter labour, spontaneous vaginal birth, decrease in analgesia use, and a decrease
in dissatisfaction with childbirth experience. Greatest benefit when provider is not a health
care professional. Continuous support was also associated with decreased likelihood to have a Cesarean or instrumental vaginal birth, regional analgesia, or a baby with a low 5 min APGAR score.
First
Second
Third
*without epidural
6-18 h
30 min-3 h 5-30 min
© Simon Ip 2009