Page 882 - TNFlipTest
P. 882
OB42 Obstetrics
Operative Obstetrics
Toronto Notes 2019
Prerequisites for Operative Vaginal Delivery
ABCDEFGHIJK
Anesthesia (adequate)
Bladder empty
Cervix fully dilated and effaced with ROM Determine position of fetal head Equipment ready (including facilities for emergent C/S)
Fontanelle (posterior fontanelle midway between thighs)
Gentle traction
Handle elevated
Incision (episiotomy)
Once jaw visible remove forceps Knowledgeable operator
A
B
C
D
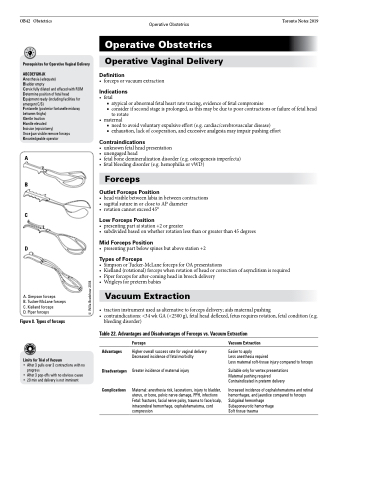
A. Simpson forceps
B. Tucker-McLane forceps C. Kielland forceps
D. Piper forceps
Figure 8. Types of forceps
Limits for Trial of Vacuum
• After 3 pulls over 3 contractions with no progress
• After 3 pop-offs with no obvious cause • 20 min and delivery is not imminent
Operative Obstetrics
Operative Vaginal Delivery
Definition
• forcepsorvacuumextraction
Indications
• fetal
■ atypical or abnormal fetal heart rate tracing, evidence of fetal compromise
■ consider if second stage is prolonged, as this may be due to poor contractions or failure of fetal head
to rotate • maternal
■ need to avoid voluntary expulsive effort (e.g. cardiac/cerebrovascular disease)
■ exhaustion, lack of cooperation, and excessive analgesia may impair pushing effort
Contraindications
• unknownfetalheadpresentation
• unengagedhead
• fetalbonedemineralizationdisorder(e.g.osteogenesisimperfecta) • fetal bleeding disorder (e.g. hemophilia or vWD)
Forceps
Outlet Forceps Position
• headvisiblebetweenlabiainbetweencontractions • sagittalsutureinorclosetoAPdiameter
• rotationcannotexceed45°
Low Forceps Position
• presentingpartatstation+2orgreater
• subdividedbasedonwhetherrotationlessthanorgreaterthan45degrees
Mid Forceps Position
• presenting part below spines but above station +2
Types of Forceps
• SimpsonorTucker-McLaneforcepsforOApresentations
• Kielland(rotational)forcepswhenrotationofheadorcorrectionofasynclitismisrequired • Piperforcepsforafter-comingheadinbreechdelivery
• Wrigleysforpretermbabies
Vacuum Extraction
• tractioninstrumentusedasalternativetoforcepsdelivery;aidsmaternalpushing
• contraindications:<34wkGA(<2500g),fetalheaddeflexed,fetusrequiresrotation,fetalcondition(e.g.
bleeding disorder)
Table 22. Advantages and Disadvantages of Forceps vs. Vacuum Extraction
Advantages Disadvantages Complications
Forceps
Higher overall success rate for vaginal delivery Decreased incidence of fetal morbidity
Greater incidence of maternal injury
Maternal: anesthesia risk, lacerations, injury to bladder, uterus, or bone, pelvic nerve damage, PPH, infections Fetal: fractures, facial nerve palsy, trauma to face/scalp, intracerebral hemorrhage, cephalohematoma, cord compression
Vacuum Extraction
Easier to apply
Less anesthesia required
Less maternal soft-tissue injury compared to forceps
Suitable only for vertex presentations Maternal pushing required Contraindicated in preterm delivery
Increased incidence of cephalohematoma and retinal hemorrhages, and jaundice compared to forceps Subgaleal hemorrhage
Subaponeurotic hemorrhage
Soft tissue trauma
© Willa Bradshaw 2004