Page 777 - TNFlipTest
P. 777
Toronto Notes 2019 Vertigo Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
• seePsychiatry,PS24
• notethatalcoholcanalsocauseacerebellarataxiaseparatefromthiaminedeficiency;thisataxiacanbe
due to cerebellar atrophy or alcohol polyneuropathy
Cerebellar Ataxias
Congenital Ataxias
• earlyonsetnon-progressiveataxiasassociatedwithvarioussyndromesaswellasdevelopmental abnormalities (e.g. Arnold-Chiari malformation, Dandy-Walker cysts)
Hereditary Ataxias
• autosomalrecessive:includesFriedrich’sataxia,ataxiawithoculomotorapraxia,ataxiatelangiectasia, vitamin E deficiency
■ Friedrich’s ataxia: prevalence 2/100,000; typical onset between 8-15 yr
◆ signs: gait and limb ataxia, weakness, areflexia, extensor plantar reflex, impaired proprioception
and vibration, dysarthria
◆ death in 10-20 yr from cardiomyopathy or kyphoscoliotic pulmonary restriction
• autosomaldominant:mostcommonlyspinocerebellarataxias(SCAs)(over30types,mostcommon SCAs due to CAG repeats)
■ signs: ataxia and dysarthria, chorea, polyneuropathy, pyramidal and/or extrapyramidal features, dementia
Acquired Ataxias
• neurodegeneration:e.g.multiplesystematrophy
• systemic:alcohol,celiacsprue,hypothyroidism,Wilson’s,thiaminedeficiency • toxins:carbonmonoxide,heavymetals,lithium,anticonvulsants,solvents
• vascular:infarct,bleed,basilarmigraine
• autoimmune:MS,Miller-Fischer(GBS)
Vertigo
• seeOtolaryngology,OT12
Motor Neuron Disease
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s Disease)
Definition
• progressiveneurodegenerativediseasethatcausesUMNandLMNsymptomsandisultimatelyfatal
Etiology
• idiopathic(most),genetic(5-10%familial,especiallySOD1mutation,other:C9orf72,TARDBP)
Pathology
• disorderofanteriorhorncellsofspinalcord,cranialnervenuclei,andcorticospinaltract
Epidemiology
• 5/100,000;incidenceincreaseswithage
Clinical Features
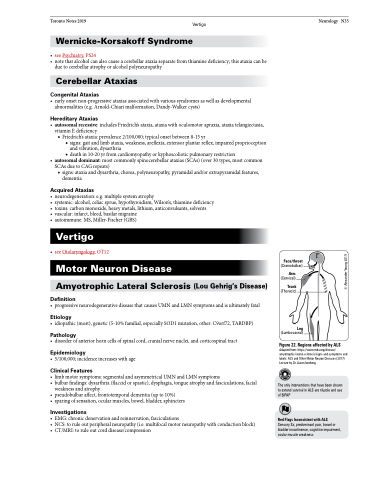
• limbmotorsymptoms:segmentalandasymmetricalUMNandLMNsymptoms
• bulbarfindings:dysarthria(flaccidorspastic),dysphagia,tongueatrophyandfasciculations,facial
weakness and atrophy
• pseudobulbar affect, frontotemporal dementia (up to 10%)
• sparingofsensation,ocularmuscles,bowel,bladder,sphincters
Investigations
• EMG:chronicdenervationandreinnervation,fasciculations
• NCS:toruleoutperipheralneuropathy(i.e.multifocalmotorneuropathywithconductionblock) • CT/MRI:toruleoutcorddisease/compression
Neurology N35
Face/throat
(Craniobulbar)
Arm
(Cervical)
Trunk
(Thoracic)
Leg
(Lumbosacral)
Figure 22. Regions affected by ALS
Adapted from: https://www.mda.org/disease/ amyotrophic-lateral-sclerosis/signs-and-symptoms and labels: ALS and Other Motor Neuron Diseases (2017) Lecture by Dr. Aaron Izenberg.
The only interventions that have been shown to extend survival in ALS are riluzole and use of BiPAP
Red Flags Inconsistent with ALS
Sensory Sx, predominant pain, bowel or bladder incontinence, cognitive impairment, ocular muscle weakness
© Alexander Young 2019